The fifth generation of wireless communication networks is brought about by the introduction of 5G technology, which represents a revolutionary moment in the telecom industry. Every new generation of wireless technology since 1G was first launched in the 1980s has brought about notable advancements in terms of speed, capacity, and functionality. But 5G promises much more than its predecessors, including the capacity to link billions of devices at once, ultra-low latency, and previously unheard-of data transmission speeds.
The next wave of technological innovation, including improved healthcare, smart cities, driverless cars, and the Internet of Things (IoT), is anticipated to be powered by 5G. 5G will transform industries, change the way we live and work, and open up new opportunities in communication and technology as the backbone of the coming digital economy.
This article examines the salient characteristics and advantages of 5G, its potential uses in diverse industries, the obstacles associated with its implementation, and the wider societal ramifications.
Recognizing 5G Technology
1. First off, what is 5G?
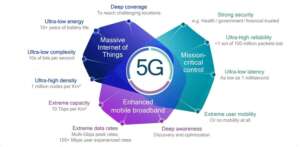
The newest standard for mobile networks is called 5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, which replaced 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution). 5G is a performance improvement above 4G, which markedly increased data throughput and mobile internet capabilities. The three primary areas of 5G advancement are as follows:
Greater data transfer speeds: Compared to 4G, 5G can send data at up to 100 times the speed, or 10 gigabits per second. This implies that customers can enjoy smooth streaming of content, download high-definition movies in a matter of seconds, and have crystal-clear video conversations.
Ultra-low latency: 5G significantly reduces latency, or the amount of time it takes for data to move between two points. 5G networks minimize latency to less than 1 millisecond, but 4G networks can have latency as high as 50 milliseconds. This makes it possible to respond in real time, which is essential for applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and driverless cars.
Massive device connectivity: Up to one million devices can be connected simultaneously in a square kilometer with 5G. This makes it perfect for the Internet of Things (IoT), which enables seamless communication between billions of connected devices, ranging from industrial sensors to smart home appliances.
2. The Main Technologies of 5G
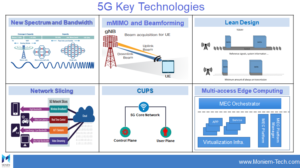
Several important technologies enable 5G’s remarkable capabilities:
Millimeter waves: 5G expands into even higher frequencies, known as millimeter waves (mmWave), which span from 24 GHz to 100 GHz. Traditional cellular networks operate in the 3-6 GHz frequency range. Faster data rates and greater bandwidth are available at these higher frequencies. They need more base stations and small cells since they have shorter ranges and are more prone to interference from structures and other barriers.
Massive MIMO (many Input, Multiple Output): MIMO technology increases network capacity and efficiency by using many antennas to send and receive more data concurrently. 5G makes use of “massive MIMO,” which increases coverage in densely populated regions and dramatically increases data speed by using a considerably greater number of antennas.
Beamforming: Using this technology, wireless signals are focused on particular devices as opposed to being dispersed throughout. By reducing interference and increasing signal strength, this focused strategy boosts the network’s overall performance.
Network slicing: With the help of 5G, operators will be able to set up several virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. Every slice can be tailored to match the unique requirements of various sectors or applications. For instance, a high-throughput slice might be set aside for video streaming, and a low-latency slice for driverless cars.
Uses of 5G in Various Industries
Beyond only providing mobile users with speedier internet, 5G has much more to offer. It will have an impact on a variety of businesses and services, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and entertainment. It has the potential to completely transform these fields.
1. Medical care
The deployment of 5G technology will be extremely beneficial to the healthcare industry. One of the most exciting uses is remote surgery, which allows doctors to use robotic devices to operate on patients remotely. 5G networks’ extremely low latency and great dependability provide real-time responsiveness, enabling surgeons to perform precise maneuvers without waiting.
5G has the potential to enable not only remote surgery but also telemedicine and virtual consultations, allowing patients to have high-quality video chats with healthcare providers from any location. This is crucial for rural communities with limited access to healthcare. Additionally, for faster diagnosis and treatment, 5G can handle the real-time transmission of massive medical data files, such MRI scans.
Real-time health monitoring and early health issue detection are made possible by the continuous collection and transmission of patient data via wearable technology and 5G-connected health monitoring equipment. This can result in less hospital visits and better patient outcomes by enabling more proactive and individualized therapy.
2. Self-Driving Cars and Transportation
With the introduction of 5G, the transportation sector will experience a significant upheaval, especially in the area of autonomous vehicle development. In order to navigate routes, avoid obstacles, and communicate with other vehicles and traffic infrastructure, self-driving cars need a continuous flow of data. These cars can process and respond to their environment in real time because to 5G’s extremely low latency and fast connectivity.
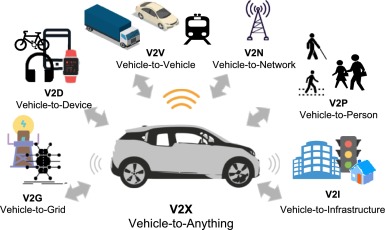
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, which allows cars to talk to pedestrians, bicycles, traffic signals, and other infrastructure (V2I), as well as to each other (V2V), will also be made possible by 5G. This networked system will maximize transportation efficiency, lessen traffic, and increase road safety.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, which allows cars to talk to pedestrians, bicycles, traffic signals, and other infrastructure (V2I), as well as to each other (V2V), will also be made possible by 5G. This networked system will maximize transportation efficiency, lessen traffic, and increase road safety.
3. Intelligent Urban Areas

5G will serve as the foundation for smart cities, which use data and technology to enhance urban life. Millions of IoT devices that can monitor and control several facets of city life, such as trash management, public safety, energy consumption, and traffic flow, have been made possible by 5G’s huge device connectivity.
For instance, real-time monitoring of traffic, noise levels, and air quality can be achieved by placing 5G-connected sensors across a city. Traffic signal optimization, pollution reduction, and resource allocation efficiency can all be achieved with the help of this data. 5G-enabled smart lighting systems can reduce energy usage by automatically adjusting brightness according to foot traffic or the time of day.
Another crucial area where 5G can have an impact is public safety. Real-time video footage analysis by surveillance cameras with AI and 5G connectivity can spot possible threats and notify authorities. Drones with 5G capabilities can be used for search and rescue operations in the event of an emergency, giving emergency responders access to real-time video and sensor data.
4. Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
With the deployment of 5G and the shift toward Industry 4.0, which prioritizes automation, data interchange, and intelligent systems in production processes, manufacturing is poised for a revolution. In 5G-enabled smart factories, sensors, robots, and machinery are networked and exchange data in real time to maximize productivity, lower downtime, and enhance product quality.
In 5G-enabled factories, robots can carry out intricate jobs more precisely, and AI-powered analytics can foresee equipment breakdowns before they happen, saving maintenance expenses. 5G’s reduced latency makes it possible for technicians to remotely operate machinery in real time, from any location in the globe.
Because 5G will allow real-time tracking of assets and shipments, it will help improve supply chain management and logistics. Manufacturers can improve production schedules, cut waste, and better satisfy customer requests with more precise data on inventory levels, delivery timelines, and demand projections.
5. Media and Entertainment

5G is expected to revolutionize the entertainment sector, especially in the areas of cloud gaming, augmented reality, and virtual reality. Immersion experiences are feasible even without costly hardware or downloads because to 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency.
Users can create more dynamic and captivating experiences by, for instance, immediately streaming VR or AR material to their devices. Because all processing will be done in the cloud, gamers will be able to stream top-notch games without the need for expensive gaming PCs or consoles thanks to 5G-powered cloud gaming platforms.
Live events and broadcasting will be transformed by 5G as well. Users may stream 4K and 8K videos on their devices and watch HD content without experiencing any buffering. Fans can utilize augmented reality (AR) applications to improve their watching experience during sporting events and concerts. Examples of these applications include virtual interactions with performers and real-time statistics.
Barriers to the 5G Deployment
Although 5G has enormous potential, there are a number of issues that need to be resolved before it can be widely used.
1. Costs of Infrastructure
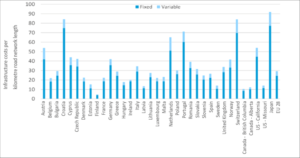
Infrastructure upgrades like as fiber-optic cables, tiny cells, and new base stations are necessary for the rollout of 5G. 5G networks need a considerably denser network of base stations to ensure appropriate coverage because millimeter waves have a shorter range than previous frequencies, especially in metropolitan areas.
It is expensive to build this infrastructure, therefore telecom companies have to weigh the necessity for investment against profitability. Governments and the commercial sector will have to work together to develop a long-term plan for financing and implementing 5G networks.
2. Assignment of Spectrum
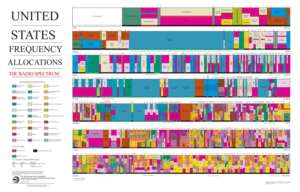
Numerous frequency bands must be available for 5G networks to function.