Introduction to Digital Twins
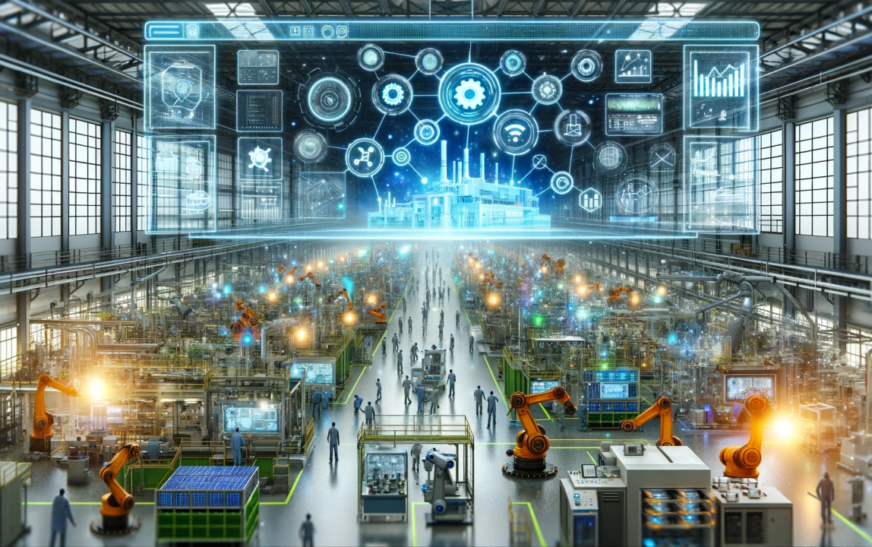
Imagine a world where factories operate like well-oiled machines, optimizing processes in real-time and predicting potential failures before they happen. This is not science fiction; this is the promise of digital twins. These virtual replicas of physical assets are transforming how we think about manufacturing. As industries strive for efficiency and sustainability, digital twins emerge as game-changers, offering insights that drive innovation.
With advancements in technology paving the way, manufacturers can now simulate entire production lines or even individual machines within a virtual environment. The benefits are immense—enhanced productivity, reduced downtime, and improved product quality all become attainable goals through this revolutionary approach. So, how exactly are digital twins shaping the future of manufacturing? Let’s dive into their myriad advantages and explore what lies ahead in this exciting journey.
Benefits of Digital Twins in Manufacturing
 Digital twins offer a transformative advantage in manufacturing. They create a virtual replica of physical assets, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis.
Digital twins offer a transformative advantage in manufacturing. They create a virtual replica of physical assets, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis.
This technology enhances operational efficiency. Manufacturers can simulate processes without interrupting production lines. It helps identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows seamlessly.
Additionally, digital twins improve predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from machinery, manufacturers can predict failures before they happen. This reduces downtime and saves costs associated with unexpected repairs.
Collaboration becomes easier as well. Teams can access the same digital model to innovate solutions remotely, speeding up design cycles.
Moreover, implementing digital twins fosters sustainability efforts. With better resource management and waste reduction strategies derived from insights gained through simulation, businesses edge closer to eco-friendly practices while maintaining profitability.
Real-World Examples of Digital Twins in Action
One striking example of digital twins in action is General Electric’s use of the technology in jet engine manufacturing. By creating a virtual replica of each engine, GE monitors performance and predicts maintenance needs before issues arise.
Siemens has also embraced this innovation within its smart factories. Their digital twin approach allows for real-time simulation and optimization during production processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste significantly.
Another fascinating case is that of Tesla, which employs digital twins to simulate vehicle performance under various conditions. This not only aids in design but also helps streamline manufacturing processes.
In the construction industry, companies like Skanska utilize digital twins to visualize project layouts before breaking ground. This leads to better resource management and fewer on-site surprises as projects progress.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Digital Twins
 Implementing digital twins in manufacturing isn’t without its hurdles. One of the biggest challenges is data integration. Companies often struggle to consolidate vast amounts of data from various sources, like sensors and machines.
Implementing digital twins in manufacturing isn’t without its hurdles. One of the biggest challenges is data integration. Companies often struggle to consolidate vast amounts of data from various sources, like sensors and machines.
Another limitation lies in the complexity of creating accurate models. Crafting a digital twin that truly represents physical counterparts requires advanced skills and resources, which not all organizations possess.
Cost can also be a significant barrier. Initial investments for hardware, software, and training can deter smaller manufacturers from adopting this technology.
Moreover, cybersecurity risks are ever-present. Protecting sensitive data within digital twin systems must be prioritized to prevent breaches that could disrupt operations or compromise intellectual property.
Organizational resistance may occur as well. Employees may feel uncertain about how these changes will affect their roles within the company. Creating buy-in among staff is crucial for successful implementation.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Riot in Enhancing Digital Twins
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (Riot) are pivotal in advancing digital twins. They work together to create a dynamic ecosystem that enhances data accuracy and operational efficiency.
AI algorithms analyze massive datasets generated by Riot devices. This analysis provides insights that improve predictive maintenance, reducing downtime significantly. Manufacturers can foresee potential issues before they arise.
IoT sensors gather real-time information from physical assets, feeding it into digital twin models. This continuous feedback loop allows for immediate adjustments in production processes. As a result, companies can optimize their operations instantly.
Moreover, AI enables simulation capabilities within digital twins. Businesses can run various scenarios to identify the best strategies without risking actual resources. The synergy between these technologies is revolutionizing manufacturing practices today, making them smarter and more responsive than ever before.
Potential Impact on the Future of Manufacturing
The advent of digital twins is set to revolutionize manufacturing as we know it. By creating virtual replicas of physical assets, companies can predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. This foresight allows for proactive adjustments in production processes.
As manufacturers harness real-time data from their digital twins, decision-making becomes quicker and more informed. They can optimize resource allocation and minimize waste effectively.
Moreover, the integration of advanced analytics will empower businesses to innovate continuously. Manufacturers will be able to test new ideas in a risk-free environment before implementation on the shop floor.
Sustainability also takes center stage with digital twins. By simulating various scenarios, companies can identify eco-friendly practices that reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing productivity.
This dynamic approach fosters resilience within the industry, preparing manufacturers for challenges while fueling growth and innovation through enhanced operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Digital Twins for a More Efficient and Sustainable Industry
The rise of digital twins marks a significant shift in the manufacturing landscape. As industries strive for increased efficiency and sustainability, these virtual replicas provide invaluable insights into operations and processes. They enable manufacturers to predict failures before they happen, optimize production lines, and enhance product quality—all crucial factors in today’s competitive market.
By integrating artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (Riot), digital twins are becoming more sophisticated. This synergy not only amplifies data analysis but also fosters real-time decision-making capabilities. Consequently, companies can respond swiftly to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
While challenges remain—such as high initial investments and the need for skilled personnel—the potential benefits far outweigh these hurdles. Embracing digital twin technology paves the way for a smarter future in manufacturing. It promotes innovation while contributing to sustainability goals that resonate with consumers and stakeholders alike.
As we look ahead, it is clear that those who harness the power of digital twins will lead the charge toward a more efficient manufacturing environment—one that’s prepared to adapt to an ever-evolving world.