Overview

Automation and machine learning (ML) are two of the 21st century’s most revolutionary technologies. Both have had a significant impact on economies, cultures, and industries. They have also accelerated the development of intelligent systems that can process vast volumes of data, make choices, and carry out activities on their own. Machine learning and automation have ushered in a new era of innovation, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across numerous sectors, from self-driving automobiles to predictive analytics in healthcare.
This article will examine the ideas, history, and practical uses of automation and machine learning, as well as how these technologies affect various industries and what obstacles they present as well as what opportunities they present.
Comprehending Machine Learning

1. Firstly, what is machine learning?
Within the field of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning is the process of creating statistical models and algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and make judgments or predictions without explicit programming. Machine learning systems use data to recognize patterns, draw conclusions, and enhance their performance over time. This is in contrast to traditional programming, where rules and logic are predefined by human programmers.
There exist multiple varieties of machine learning:
supervised instruction
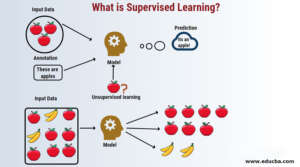
This method pairs the input data with the appropriate output, allowing the model to be trained on a labeled dataset. After being trained, the algorithm may anticipate new, unseen data by learning to link the inputs to the matching outputs.
Unsupervised learning: In unsupervised learning, the model searches the unlabeled data for buried relationships or patterns. In unsupervised learning, clustering and dimensionality reduction are often employed methods.
Reinforcement learning: In this kind of learning, an agent engages with its surroundings and gains decision-making skills through the application of rewards or punishments. The agent seeks to maximize its cumulative reward over time, which prompts the formulation of ideal plans of behavior.
2. Machine Learning’s Development
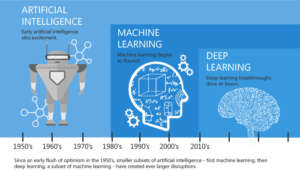
The early stages of artificial intelligence development are where machine learning originated. The phrase “machine learning” was first used in 1959 by AI pioneer Arthur Samuel, who was developing a software to play checkers. One of the first instances of machine learning in action, his algorithm evolved over time by taking lessons from the results of earlier games.
With the creation of algorithms like decision trees and neural networks in the decades that followed, machine learning made tremendous advancements. But it wasn’t until the large-scale data, higher processing power, and improvements in statistical techniques of the 1990s and early 2000s that machine learning started to make significant strides in practical applications. Its development was further expedited by the advent of big data and cloud computing, which allowed machines to process enormous datasets and extract insights that were unthinkable before.
Personalized recommendations, natural language processing (NLP), facial recognition, and many other cutting-edge technologies today are powered by machine learning.
Automation and Machine Learning: Their Interaction

1. First, What Exactly Is Automation?
Automation is the use of technology to carry out operations or jobs with little or no assistance from humans. Automation can encompass a wide range of applications, from straightforward rule-based systems like email sorting to intricate autonomous systems like self-driving cars. Automation aims to maximize productivity, decrease human error, and boost efficiency.
Automation has been around for a while, especially in industrial and manufacturing processes, but a new class of intelligent automation systems has been made possible by its combination with machine learning. More adaptable and powerful automation solutions can result from these systems’ capacity to learn from new data, adjust to changing conditions, and make decisions instantly.
2. Machine Learning-Based Intelligent Automation
The next phase of technological development is represented by the fusion of automation with machine learning, sometimes known as intelligent automation or cognitive automation. This paradigm uses machine learning techniques to improve automation systems so they can manage jobs that are increasingly complicated and adjust to unexpected events.
In conventional automation, for instance, a robotic arm on a manufacturing floor might be trained to consistently carry out a certain activity, like constructing a product. But using machine learning, the robotic arm may gradually learn to improve its speed, accuracy, and adaptability by evaluating data from sensors. Similar to this, chatbots with machine learning capabilities in customer service can comprehend and reply to a variety of consumer inquiries, enhancing their capacity to manage increasingly complicated conversations without the need for human intervention.
Uses of Automation and Machine Learning

1.Medical Care
Healthcare could undergo a transformation thanks to automation and machine learning, which could also streamline administrative procedures and improve diagnosis and treatment personalization. One of the most promising fields where machine learning is already having a big influence is medical imaging. With accuracy on par with human radiologists, algorithms trained on massive datasets of medical scans, including MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays, can identify conditions like brain tumors, pneumonia, and cancer. These algorithms can help physicians diagnose patients more quickly and accurately, which can result in early treatment and better patient outcomes.
Another area where machine learning is being utilized to enhance healthcare is predictive analytics. Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze patient data and forecast the risk of developing specific ailments, such diabetes or heart disease, so physicians can take preventive action. Machine learning is used in personalized medicine to customize medicines for each patient based on their genetic composition, way of life, and past medical records. This increases treatment efficacy and lowers the possibility of unfavorable side effects.
Administrative duties in the healthcare industry, such as making appointments, handling insurance claims, and keeping track of patient information, are becoming more efficient thanks to automation. Healthcare practitioners can lessen their paperwork load and concentrate more on patient care by automating these processes.
2. Industry and Manufacturing

Although automation has always been a pillar of the manufacturing sector, machine learning integration is elevating industrial automation to new levels. One of the most useful uses in this field is machine learning-powered predictive maintenance. Machine learning models can forecast when equipment is likely to break and suggest maintenance before a breakdown happens by evaluating data from sensors integrated into machinery. This lowers downtime, increases machine longevity, and saves money on maintenance and lost output.
Another area where automation and machine learning are having an impact is quality control. Human inspection, which might be labor-intensive and error-prone, was a major component of quality control in the industrial industry in the past. These days, real-time picture analysis of products using machine learning algorithms can identify anomalies or flaws, increasing the precision and effectiveness of quality control procedures.
Supply chain optimization is a part of manufacturing automation. To improve inventory management and cut expenses, machine learning models can evaluate data on supply and demand, manufacturing schedules, and transportation logistics.
3. Autonomous cars and transportation

The creation of autonomous vehicles is one of the most fascinating and well-known uses of automation and machine learning. Leading companies in the development of self-driving cars, such as Tesla, Waymo, and Uber, rely on machine learning algorithms to navigate highways, avoid obstacles, and make judgments in real-time. To understand their environment and drive safely, these cars use a variety of sensors, cameras, radar, and machine learning.
Autonomous vehicles have the ability to decrease pollution, enhance traffic flow, and lessen accidents brought on by human mistake. They do, however, also confront formidable obstacles, including as legal restrictions, moral dilemmas, and technological constraints when managing intricate driving situations.
Automation and machine learning are being used in logistics and transportation, not just in self-driving cars. For instance, shipping companies utilize machine learning algorithms to improve delivery routes, which lowers fuel usage and delivery times. Automation systems with machine learning capabilities in warehouses may handle inventory, complete orders, and even control autonomous robots that transport goods from one location to another.
4. Banking and Finance

Machine learning and automation have been quickly adopted by the banking and finance industries in an effort to boost productivity, lower fraud, and improve client experiences. One of the most significant uses of machine learning in finance is fraud detection. Machine learning algorithms are able to detect odd patterns or behaviors in transaction data that can point to illicit activities, including credit card fraud or identity theft. These models have the ability to identify fraud in real time, which gives financial institutions the ability to safeguard consumers right now.
Another field where machine learning has advanced significantly is algorithmic trading. Machine learning models are used in algorithmic trading to evaluate market data, spot trading opportunities, and quickly execute transactions. To help traders make wise judgments, these algorithms can process enormous volumes of data, such as news, economic indicators, and stock prices. Although algorithmic trading can yield substantial profits, there are hazards associated with it as well, since quick, automated trades can increase market volatility.
In banking, automation is also improving customer service. Machine learning-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are being used to handle standard consumer requests, including processing transactions, verifying account balances, and offering financial advice. By decreasing the workload for human personnel and offering prompt, efficient service, this increases customer satisfaction.
Difficulties and Ethical Issues
Automation and machine learning have many advantages, but they also come with a number of drawbacks and moral dilemmas.
1. Displacement from Work

The possibility of employment displacement due to automation is one of the most important worries. There is a rising concern that automation will result in widespread unemployment as computers and algorithms become more adept at carrying out tasks that have historically been completed by people. Automation is especially dangerous for jobs in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and customer service.
Many experts contend, however, that although automation will remove certain employment, it will also open up new opportunities. For instance, there is a growing need for qualified experts in disciplines like data science, AI ethics, and machine learning engineering due to the advent of machine learning and AI. Making sure that employees have access to the education and training required to move into these new professions will be a challenge.
2. Machine Learning’s Bias and Fairness

The quality of machine learning models depends on the data they







