Imagine a world where every step of your favorite products’ journey is transparent and secure. This isn’t just a dream—it’s the reality that block chain technology is creating, particularly in supply chain management. As businesses strive for greater efficiency and transparency, they are discovering how the block chain is disrupting traditional processes to enhance accountability and traceability.
From tracking raw materials to ensuring ethical sourcing, block chain’s decentralized nature offers a game-changing solution that could redefine industry standards. Gone are the days of convoluted paperwork and lack of visibility; now it’s all about real-time data sharing among stakeholders. Join us as we explore how this innovative technology is reshaping supply chains across multiple sectors, unlocking new levels of efficiency and trust like never before.
What is block chain?
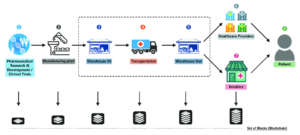 Block chain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. This unique structure ensures that once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from all participants.
Block chain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. This unique structure ensures that once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from all participants.
At its core, block chain operates through a series of blocks linked together in chronological order. Each block contains data, timestamps, and cryptographic hashes connecting it to the previous block. This creates an immutable chain of records.
One of block chain’s standout features is transparency. Every participant has access to the same information simultaneously, providing unmatched visibility into processes and transactions.
Additionally, the use of smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded onto the blockchain—automates processes further. This reduces human error while enhancing efficiency in various applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chains and logistics management.
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the backbone of modern commerce. It encompasses the entire journey of a product, from raw materials to finished goods reaching consumers. This complex web involves various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
The goal of SCM is efficiency. Streamlining processes ensures that products are delivered on time and at lower costs. Coordination between these parties can greatly enhance customer satisfaction.
Today’s global marketplace adds layers of complexity to supply chains. Businesses face challenges such as fluctuating demand and geopolitical factors that impact delivery routes.
Technology plays a pivotal role in addressing these issues. Innovative solutions are essential for transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain process.
With increasing consumer expectations for speed and reliability, companies must adapt their strategies constantly to stay competitive in this dynamic environment.
How Block chain is Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
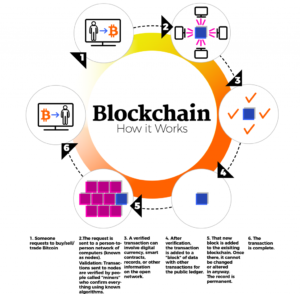 Block chain is changing the landscape of supply chain management in profound ways. It introduces transparency that has been elusive in traditional systems. Every transaction becomes an immutable record, allowing stakeholders to track products from origin to destination.
Block chain is changing the landscape of supply chain management in profound ways. It introduces transparency that has been elusive in traditional systems. Every transaction becomes an immutable record, allowing stakeholders to track products from origin to destination.
With block chain, data sharing among partners happens seamlessly. This means fewer misunderstandings and faster decision-making processes. As a result, businesses can respond more quickly to market demands.
Additionally, the technology enhances security against fraud and tampering. Each participant in the supply chain has access to verified information without relying on a central authority. This decentralized approach fosters trust among all parties involved.
Furthermore, smart contracts automate various processes within the supply chain. These self-executing contracts reduce paperwork and streamline operations significantly. The efficiency gained here cannot be overstated; it directly impacts profitability and customer satisfaction alike.
Advantages of Using Block chain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology offers transparency in supply chain management. Every transaction is recorded in a decentralized ledger, accessible to all parties involved. This visibility fosters trust among stakeholders.
Security is another key advantage. Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered easily. This immutability protects against fraud and unauthorized changes.
Efficiency also sees a boost with blockchain integration. Automated processes reduce paperwork and streamline operations, leading to faster transactions and lower costs.
Additionally, traceability becomes seamless. Companies can track products from origin to consumer effortlessly, ensuring authenticity and compliance with regulations.
Enhanced collaboration emerges as different entities share real-time information securely on the same platform. This synergy enables quicker decision-making across the entire supply chain network.
Real-Life Examples of Companies Utilizing Blockchain in SCM
Walmart is a leading example of blockchain’s impact on supply chain management. The retail giant uses blockchain to enhance food safety. By tracking produce from farm to shelf, they can quickly identify sources of contamination.
Another notable case is Maersk, which partnered with IBM to streamline global shipping processes. Their platform reduces paperwork and speeds up transactions, making logistics more efficient and secure.
De Beers also embraces this technology by ensuring diamond provenance. Customers gain confidence knowing their purchases are conflict-free through transparent tracking systems.
Additionally, Nestlé utilizes blockchain for transparency in sourcing ingredients like coffee and cocoa. This initiative builds consumer trust while promoting sustainable practices.
These companies showcase the versatility of blockchain in enhancing operational efficiency across diverse industries within supply chain management. Each implementation highlights unique challenges addressed and benefits gained through innovative solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Blockchain in SCM
Implementing blockchain in supply chain management comes with its own set of challenges. One major hurdle is the lack of standardization across various industries. Each sector may have different requirements, making it difficult to establish a unified blockchain framework.
Cost is another significant factor. The initial investment for integrating blockchain technology can be substantial. Smaller businesses might struggle to allocate resources toward this transition.
Moreover, scalability poses an issue as well. Many existing blockchain networks are not equipped to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently, which can lead to delays and increased processing times.
Data privacy concerns cannot be overlooked either. While transparency is one of the key benefits of blockchain, sharing sensitive information among multiple parties raises questions about confidentiality and security.
Resistance from stakeholders within traditional systems adds complexity. Change often meets skepticism; convincing established players in the supply chain to adopt new technologies can be a daunting task.
Future Implications and Potential for Growth in the Industry
The future of supply chain management is poised for transformative changes driven by blockchain technology. As companies increasingly recognize its benefits, adoption rates are expected to soar.
Enhanced transparency will foster trust among stakeholders. This could lead to stronger partnerships and more transparent transactions across the board.
Moreover, smart contracts—self-executing agreements with terms directly written in code—can streamline operations. They eliminate delays caused by paperwork and manual processes.
As industry standards evolve, interoperability between different blockchain systems will emerge as a key focus. This interconnectedness can create a seamless flow of information across various platforms, enhancing efficiency.
Sustainability also stands to gain traction through blockchain’s traceability features. Companies committed to ethical sourcing will find it easier to prove compliance.
With ongoing innovations and increased investment, the potential for growth in this sector remains vast. The landscape is shifting rapidly, making it an exciting time for supply chain professionals worldwide.
Conclusion
Blockchain is changing the landscape of supply chain management in profound ways. Its decentralized nature provides transparency and trust, essential elements for efficient operations. Companies are starting to realize the benefits of tracking products in real-time, reducing fraud, and improving overall efficiency.
As businesses adopt blockchain technology, they gain a competitive edge by enhancing credibility with customers and partners alike. The potential for growth in this area is immense. Supply chains that leverage blockchain can not only streamline processes but also create more sustainable practices.
The road ahead may have challenges, but the momentum is clear. Embracing this innovation could very well define the future of supply chain management across various industries. As organizations adapt to these changes, we are likely to witness a transformation that will make supply chains smarter and more resilient than ever before.








