Overview

Social media’s emergence in the latter half of the 20th century was a turning point in human communication that permanently changed the way people interacted with one another and with communities and enterprises. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, and others have grown quickly, creating an interconnected world where people can share ideas, content, and information instantly with others all over the world. But this surge is more than just a technological development; it is also a profoundly changing society
This essay delves into the beginnings, development, and significance of social media, charting its course from the 1990s to the present. It also looks at the significant impacts that social media has had on a range of areas, including politics, business, culture, and interpersonal relationships.
The History of Social Media
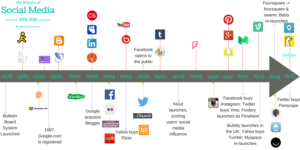
1. The Initial Period: the 1990s
Although social media did not really take off until the early 2000s, its roots may be found in the 1990s. Online communication was made possible by Tim Berners-Lee’s creation of the World Wide Web in 1989. Early social networking services and online communities gained popularity in the 1990s.
Six Degrees was one of the first significant platforms, having debuted in 1997. Its restricted functionality and small user base prevented it from becoming a mainstream sensation, despite the fact that it let users to establish profiles, list friends, and share information within a network. AOL Instant Messenger (AIM) and ICQ gained popularity as real-time online chat platforms around the same period. These early platforms included important features that would later define the space, such as online profiles, networks of friends, and immediate communication, even though they lacked the interactivity and multimedia capabilities of contemporary social media.
In the latter part of the 1990s, blogging gained popularity as well. Websites such as LiveJournal and Blogger allowed users to express their ideas, opinions, and information to a larger audience. These technologies promoted user-generated content and early online expression, which were forerunners of the social media platforms that would soon take over the digital world.
2. The Early 2000s: When Social Media Giants Started to Emerge

The real start of the social media boom came in the early 2000s. MySpace was one of the first social networking sites to become well known after it was introduced in 2003. MySpace gave users the opportunity to make unique profiles, interact with friends, and exchange blogs, images, and music. Its emphasis on self-expression and configurable interface made it especially appealing to musicians and younger users, which contributed to its explosive growth.
However, Facebook—which Mark Zuckerberg and his roommates at Harvard University founded in 2004—was the social media platform that really transformed the industry. Facebook’s user base rapidly grew from its initial restriction on college students, and by 2006, anyone over the age of 13 could sign up. Facebook’s real-name policy, simple interface, and ability to post updates, pictures, and videos with friends all contributed to the social media platform’s growth. It changed the way individuals engaged with each other on the internet, shifting the focus from anonymity to a more intimate, linked experience.
Soon after, more websites popped up, such as the professional-focused LinkedIn (2003) and the photo-sharing-focused Flickr (2004). These sites, which cater to various user demographics and interests, varied the social media scene.
Social Media’s Development

1. From 2006 to 2010: The Ascent of Multimedia Sharing and Twitter

The introduction of Twitter in 2006 marked the next significant advancement in the social media sphere. Twitter users could publish 140-character messages, or “tweets,” unlike on other sites. Because of its emphasis on real-time sharing and interaction, microblogging has become the go-to site for news updates, celebrity interactions, and live event commentary. Later on, Twitter’s real-time feature would become increasingly important in influencing conversations around the world, especially during political movements and crises.

As multimedia information became more and more popular, social media kept changing as well. Since its introduction in 2005, YouTube has become the most popular site for sharing videos. In addition to revolutionizing the way people consume material, YouTube gave rise to a new class of content creators known as “YouTubers,” who went on to become well-known names in marketing, education, and entertainment.
Around this time, social media started to change due to the influence of mobile technologies. Users were able to access social media on the go because to the 2007 debut of the iPhone and the widespread use of smartphones, which enhanced participation and real-time interaction.
2. Instagram, Snapchat, and the Visual Content Age, 2010-Present
The number of new social media platforms exploded in the 2010s, with many of them emphasizing visual material. With its straightforward design and emphasis on aesthetics, Instagram, a photo-sharing software that debuted in 2010, immediately became well-known. Instagram appealed especially to younger users and brands trying to establish their brand because of its emphasis on visual storytelling and the ability to apply filters and hashtags.

Disappearing content is another novel idea that Snapchat brought to social media with its 2011 launch. Users who were looking for more fleeting, informal methods to express their daily lives found resonance in its brief “Stories” feature, where posts disappear after a 24-hour period. Due to its popularity among younger audiences, Snapchat was able to demonstrate the growing desire for impromptu, short-lived content. Facebook and Instagram soon followed suit, introducing their own “Stories” capabilities.

TikTok, a short-form video platform that went widespread in the mid-2010s thanks to its easy-to-use video editing features and engaging content, also rose to prominence in this period. Because of its algorithm, which provides users with tailored material based on their interests, TikTok has amassed a sizable global user base quite quickly, especially among Generation Z. The platform became a cultural phenomenon due to its emphasis on music, dance, challenges, and memes; this further solidified the dominance of video content on social media.
Social Media’s Effect

1. Interaction and Bonding
The way people communicate has been drastically altered by social media. Social media sites like Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook have made it simpler than ever to maintain relationships with loved ones no matter how far away you live. Social media has replaced many people’s other key sources of relationship maintenance, life event sharing, and activity updates.
But the ease of communication has also raised worries about the demise of in-person connections and surface-level exchanges. Excessive usage of social media can lead to feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression, according to studies. This is because users may compare their lives to the well managed and frequently idealized representations of others’ lives that they see online. Stress and social media addiction can also be caused by the need to project a flawless image.
In addition, social media has given rise to new kinds of connections, especially through interest-based groups and online communities. Social media sites such as Reddit, Discord, and Facebook Groups facilitate global connections between users and like-minded people, creating communities centred around common interests, pastimes, or causes.
2. Commercial and Advertising

Businesses and marketing have also been significantly impacted by the social media boom. Businesses now view social media as an essential resource for connecting and interacting with their clientele. Social media platforms give companies direct contact to customers, enabling them to market their goods, get customer feedback, and foster brand loyalty.
One of the biggest developments in social media marketing is the emergence of influencer marketing. Influencers, or people with sizable fan bases on social media sites like Instagram and YouTube, have developed into effective marketing resources for companies targeting particular audiences. Influencers’ endorsements are frequently more powerful than traditional advertising because of their relatability and genuineness.
Furthermore, social media advertising has grown to be a successful sector of the economy on its own. Businesses can target consumers based on their interests, activities, and demographics by utilizing the advanced ad targeting technologies available on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn. Modern marketing strategy must include social media advertising since it is more targeted and cost-effective than conventional media.
3. The Social Movements and Politics
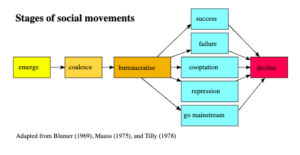
Social media has revolutionized political and social movement dynamics. Politicians, activists, and regular people may now communicate their opinions, plan events, and rally support via social media sites like Facebook and Twitter. Social media’s real-time nature has made it possible for users to participate in public debates and follow political developments as they happen.
Social media has played a significant role in the propagation of movements such as the Arab Spring (2010–2012), #BlackLivesMatter, and #MeToo. These platforms have enabled activists to mobilize people worldwide, garner support, and subvert established hierarchies. Social media is a potent driver for social change because of its capacity to magnify voices that might otherwise go unheard.
Social media has, meanwhile, also come under fire for its part in the dissemination of false information and fake news, especially during election seasons. For instance, claims of foreign meddling and the dissemination of misleading material on social media sites like Facebook and Twitter brought attention to the negative aspects of social media during the 2016 U.S. presidential election. Concerns over the need for more regulation and increased accountability from social media businesses have grown as a result of this.
Difficulties and Fears
Social media has numerous advantages, but it also has a lot of drawbacks. Privacy is one of the most important topics. People frequently divulge personal information without fully realizing the ways in which social media firms, advertising, or other third parties may exploit it. Concerns over security and privacy in the digital era have been brought up by data breaches and the improper use of personal information.
Furthermore, worries regarding mental health have arisen as a result of social media’s addictive qualities. Likes, comments, and shares indicate a continuous demand for validation, which can lead to worry and feelings of inadequacy. Other significant issues include the proliferation of false information, cyberbullying, and the emergence of “echo chambers,” when people are only exposed to material that confirms their preconceptions.







